

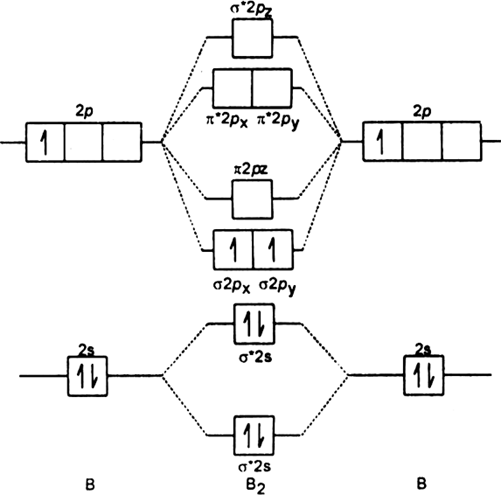
The stability of multi-electron atom is due to the bigger magnitude of attractive force between nucleus and electrons as compared to the forces of repulsion between electrons of the inner shell and outer shell. However, the energy of an electron in multi-electron atoms depends on both its principal quantum number (n) and its azimuthal quantum number (l). The order of size is 1s < 2s < 3s <, as shown below. The bond order can be determined for this molecule. The atomic orbitals that combine are of similar energy levels a 1s orbital does not combine with one of the 2s orbitals. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. Similarly 2s atomic orbitals combine, giving a bonding orbital and an antibonding orbital, which are filled with the remaining valence electrons starting from the bottom up. Here, 6s,5p and 4d have 5,4 and 3 total number of nodes respectively. An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. Orbitals can be ranked in the increasing order of orbital energy as follows: 1s < 2s 2p < 3s 3p 3d <4s 4p 4d 4f. Total number of nodes is given by the sum of radial nodes and angular nodes.
An orbital is a region of space where there is a high probability of finding an electron. Within a given principal quantum number, the energy of orbitals increases in the order s The reason behind different energies between the various subshells of the same shell is that there exists a mutual repulsion among the electrons in multi-electron atoms. The energy of an electron in a single atom can be determined solely by the principal quantum number. Current theory suggests that electrons are housed in orbitals. For a given principal quantum number, s, p, d, f.The energy of the orbital in multi-electron atoms depends on angular momemtum quantum number as well as Principle quantum number.An electron in the 2s, 2p or higher orbitals in a hydrogen atom is in excited stateĮnergy of Orbital in multi-electron atoms We can combine the atomic orbitals of atoms in. The Schrodinger equation dictates the energy order of the orbitals: (but they can be readily determined by looking at the periodic table or using a simple. The word ‘Aufbau’ in German means ‘Building up’. Atomic orbitals describe the probability of finding a given electron of an atom in a given region of space. the orbital with the lowest energy will be filled first and the orbital with the highest energy will be filled first.
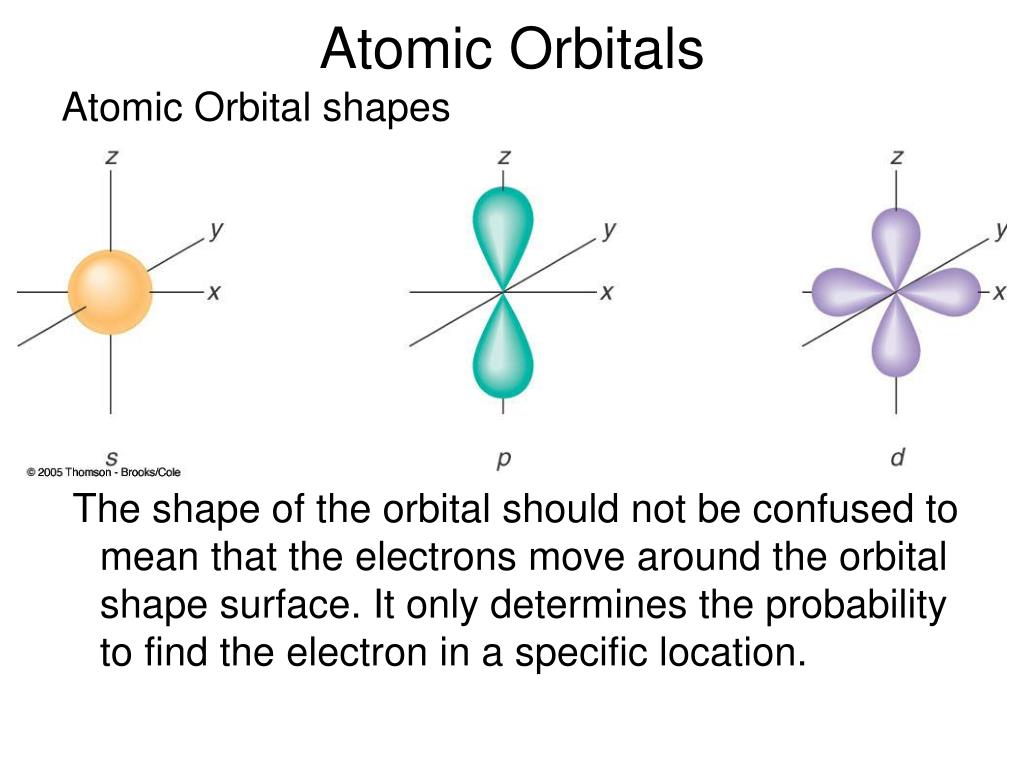
The 1s orbital in a hydrogen atom is the most stable condition and is called the ground state and an electron residing in this orbital is most strongly held by the nucleus. The electrons in different orbitals are filled in the increasing order of their energy, i.e.Orbitals having the same energy are called degenerate orbitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
